Russia's Growing Sahel Influence a Worry for Jittery West
ANTI-IMPERIALISM
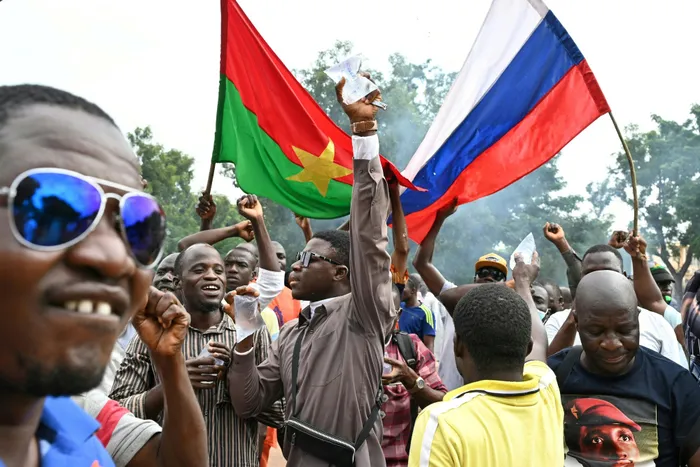
SUPPORTERS of Burkina Faso’s leader, Ibrahim Traore, demonstrate their support for Russia in Ouagadougou. The termination of the French and US missions in the Sahel countries was framed as an assertion of sovereignty and independence from erstwhile colonisers and contemporary neo colonial and imperial forces to make it more politically appealing to the citizens of these countries, says the writer.
Image: AFP
Dr. Sizo Nkala
RUSSIAN influence in the Sahel region has been on the rise since the coup wave of recent years.
The junta leaders in Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger who seized power in 2021, 2022, and 2023 respectively, wasted little time in severing relations with their erstwhile colonizer, France, while embracing Russia.
In 2022, Mali terminated the French-led Operation Barkhane, which saw about 2400 French troops withdrawing from the country as the Assimi Goita-led military junta argued that the operation had not been effective in its ten-year battle against the Islamist insurgency. His counterparts, Ibrahim Traore in Burkina Faso and Abdourahamane Tchiani in Niger followed suit kicking out French troops out of their countries in 2023 citing their failure to stamp out jihadist insurgencies.
Public rallies were organized in Niger to add public pressure on the French troops. Rally attendees were waving Russian flags and chanting Russian affirmations. About 1000 US troops also stationed in Niger for counterinsurgency purposes withdrew from the country in 2024 at the instigation of the military junta.
The termination of the French and US missions in the Sahel countries was framed as an assertion of sovereignty and independence from erstwhile colonisers and contemporary neocolonial and imperial forces to make it more politically appealing to the citizens of these countries.
Seeing an opportunity to establish a geostrategic foothold, Russia, through its proxy mercenary outfit – the Wagner Group (now rebranded the Africa Corps) – swiftly moved to fill in the vacuum promising to deal ruthlessly with the jihadist insurgents riding on the back of its relative success in the Central African Republic (CAR) where it helped to defend the Faustin-Archange Touadera regime against the rebels.
The African Corps is fully funded by the Russian state, which makes them an instrument of Moscow’s foreign policy in Africa. Russia also relies on its history of supporting anti-colonial liberation movements in Africa to portray itself as a trustworthy partner compared to the West, which cannot shake off the coloniser tag.
Moreover, facing Western isolation over the Ukraine war, Russia desperately needed diplomatic allies in Africa. Its active support of and military presence in the three Sahelian states is an attempt to project its power in Sub-Saharan Africa and show its commitment to the peace and security of the continent in the hopes of swaying more African countries to its side in its standoff with the West.
Apart from the diplomatic support, Moscow is also interested in establishing economic relationships with the Sahelian states which boast major reserves in gold (Burkina Faso) and uranium (Niger). Burkina Faso, which has been turning the screws on western mining companies operating in the country, recently granted a Russian firm, Nordgold, an industrial mining license to conduct operations in the Kourweogo province.
About 1500 members of the Group arrived in Mali at the beginning of 2022 following an invitation from Assimi Goita to help repel the insurgents, who had wreaked havoc in the West African country since 2017. Goita and his allies had seized power on the promise that they would eliminate the rebels and stabilise the security situation in the country.
Soon after it changed its name to Africa Corps, 100 members of the group landed in Burkina Faso to help Traore’s government fight the insurgents in January 2024. Niger received its own contingent of Africa Corps a few months later with the same mandate.
Thus, Russia has effectively replaced France and the US as an alternative security partner and political patron for the Sahelian states. In addition to the presence of its mercenary company, Russia has also become an important arms supplier for the three countries.
Since 2021, Mali has received significant amounts of Russian military equipment including over 100 military vehicles, helicopter gunships, military jets and ammunition. Burkina Faso has received military instructors from Russia to train its security personnel. In a major diplomatic move, the foreign ministers of the three countries travelled to Russia early in April under the aegis of the Alliance of Sahel States (AES) to strengthen the alliance’s relationship with Russia.
Their meeting with the Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov yielded a commitment by Moscow to support the 5000 strong joint force established by the three juntas to address the security challenges in the region. This force is founded on the mutual defence pact signed by the three countries in 2023.
Ultimately, the utility of this new security partnership will be judged on its ability to contain and suppress the jihadist insurgents. Thus far, the new partnership has not made significant inroads in addressing the security situation. According to the Global Terrorism Index 2025 report, Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger are in the top 5 countries most affected by terrorism in the world.
* Dr. Sizo Nkala is a Research Fellow at the University of Johannesburg’s Centre for Africa-China Studies.
** The views expressed do not necessarily reflect the views of IOL, Independent Media or The African.